Endophytic fungi are a key component of sustainable agriculture, as they live within plant tissues without causing harm, contributing to their resistance to stress and pathogen attack. In this article, we will explore what endophytic fungi are, their main benefits, prominent species, and how to harness them in agricultural management.

What are endophytic fungi?
Endophytic fungi are microorganisms that colonize the interior of plants asymptomatically. This symbiotic coexistence strengthens the plant against adverse environmental conditions, improving its tolerance to biotic and abiotic stress.
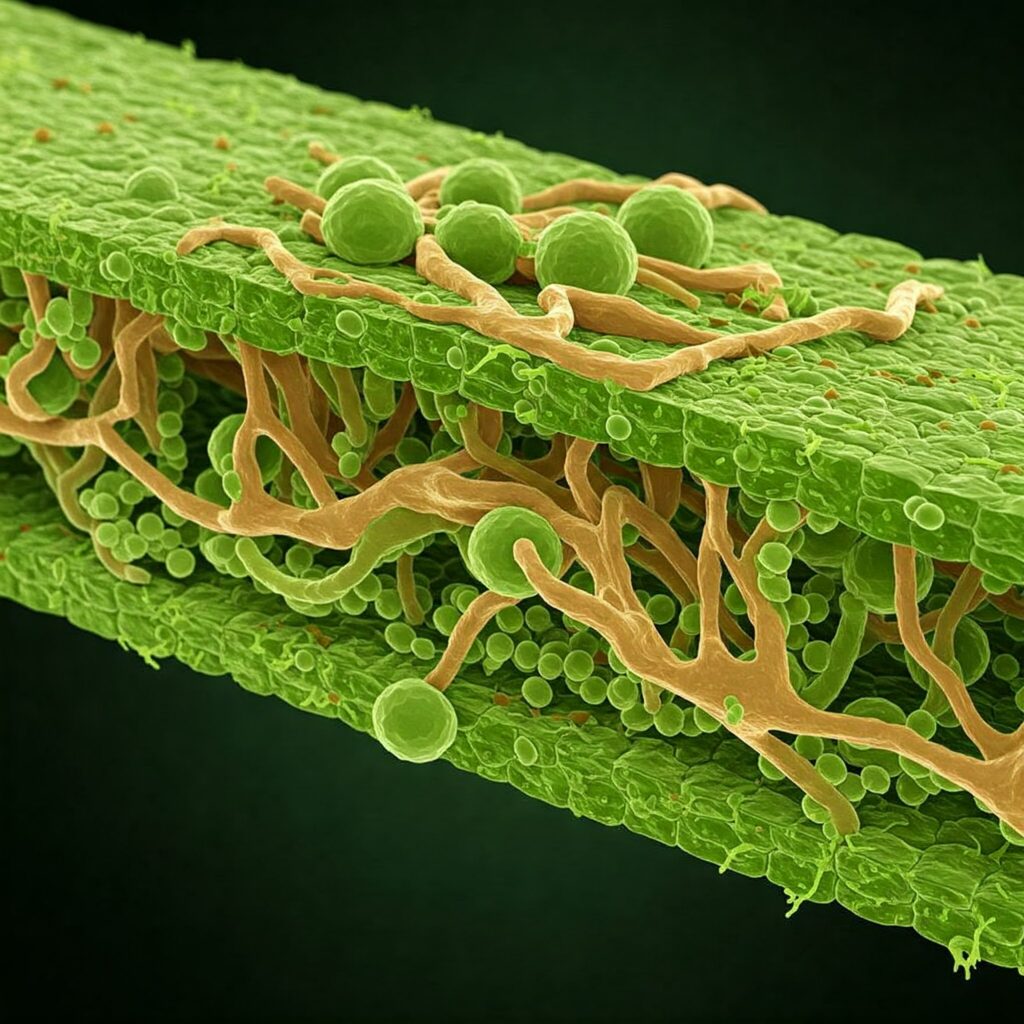
Main species of endophytic fungi and their characteristics
These are some of the most commonly used endophytic fungi in modern agriculture:
- Piriformospora indica: Improves tolerance to abiotic stress such as drought and salinity, increasing root production.
- Serendipita vermifera: Benefits the growth of crops like wheat and barley, especially in nitrogen-poor soils.
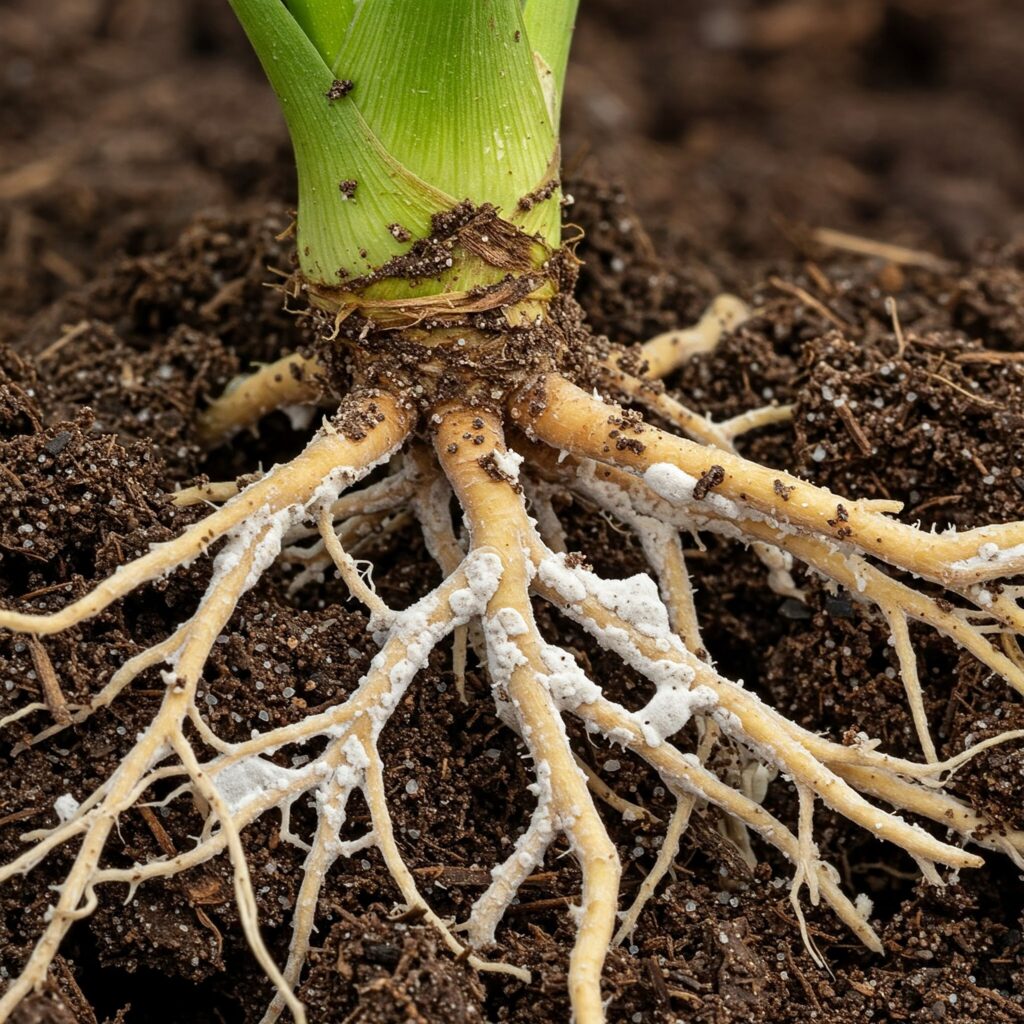

Benefits of endophytic fungi in agriculture
Including endophytic fungi in agricultural systems offers multiple advantages that are reflected in the health and productivity of crops:
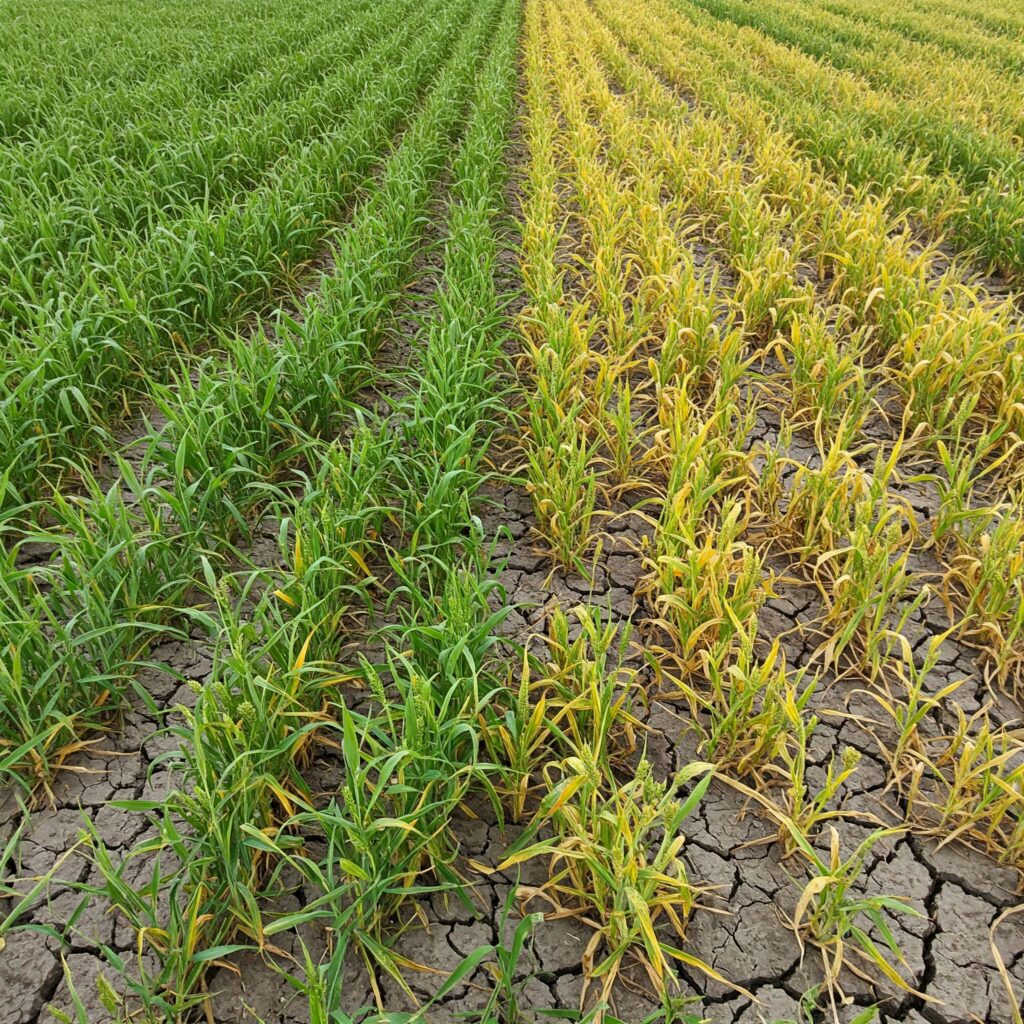
- Resistance to environmental stress: Plants colonized by endophytes better withstand drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures.
- Yield increase: They improve nutrient use efficiency and promote root growth.
- Protection against pathogens: They generate antimicrobial compounds that limit the development of pathogenic fungi in the roots.
- Greater water efficiency: The association with endophytic fungi favors water retention in the roots.
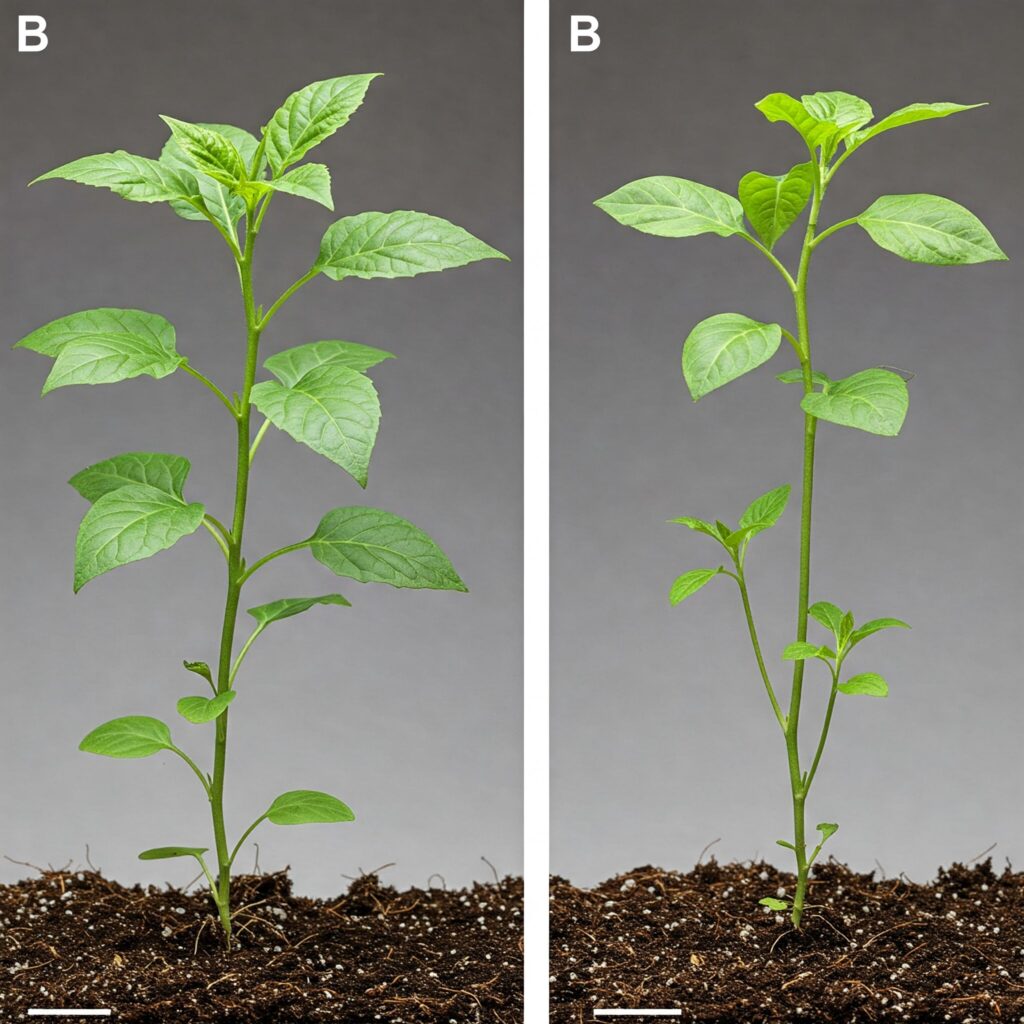

Practical implementation in agricultural crops
To maximize the benefits of endophytic fungi, the use of bioinoculants containing viable spores is recommended. It is essential to apply them during the early growth stage to ensure their effective colonization.

Conclusion
Endophytic fungi represent an innovative strategy to improve the resilience of crops against environmental changes and diseases. Integrating them into agricultural systems allows for the optimization of yield naturally, reducing the dependence on chemical inputs.

References
- Rodriguez, R. J., et al. (2009). Fungal endophytes: diversity and functional roles. New Phytologist, 182(2), 314-330.
- Waller, F., et al. (2005). The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica reprograms barley to salt-stress tolerance. Plant Physiology, 139(2), 1007-1017.
 AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog
AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog 


