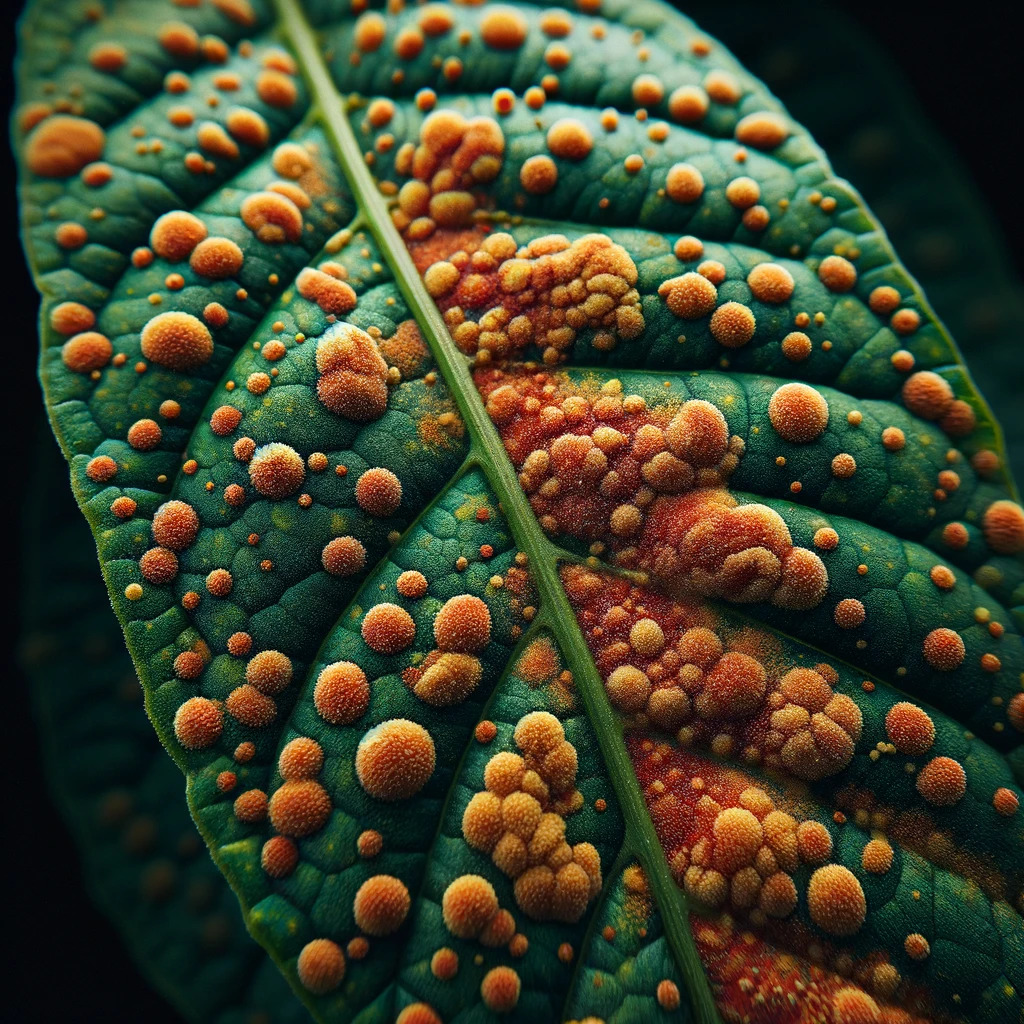
Understanding Rust, the Persistent Challenge in Agriculture
Rust is a fungal disease that affects a wide variety of crops, posing a significant concern for farmers. Characterized by reddish or yellowish pustules on leaves, rust can significantly reduce crop yield and quality.
What is Rust and How is it Identified?
Rust is caused by various types of pathogenic fungi that create rust-like spots on plant leaves and stems. These spots, or pustules, release spores that spread rapidly, especially in humid conditions.
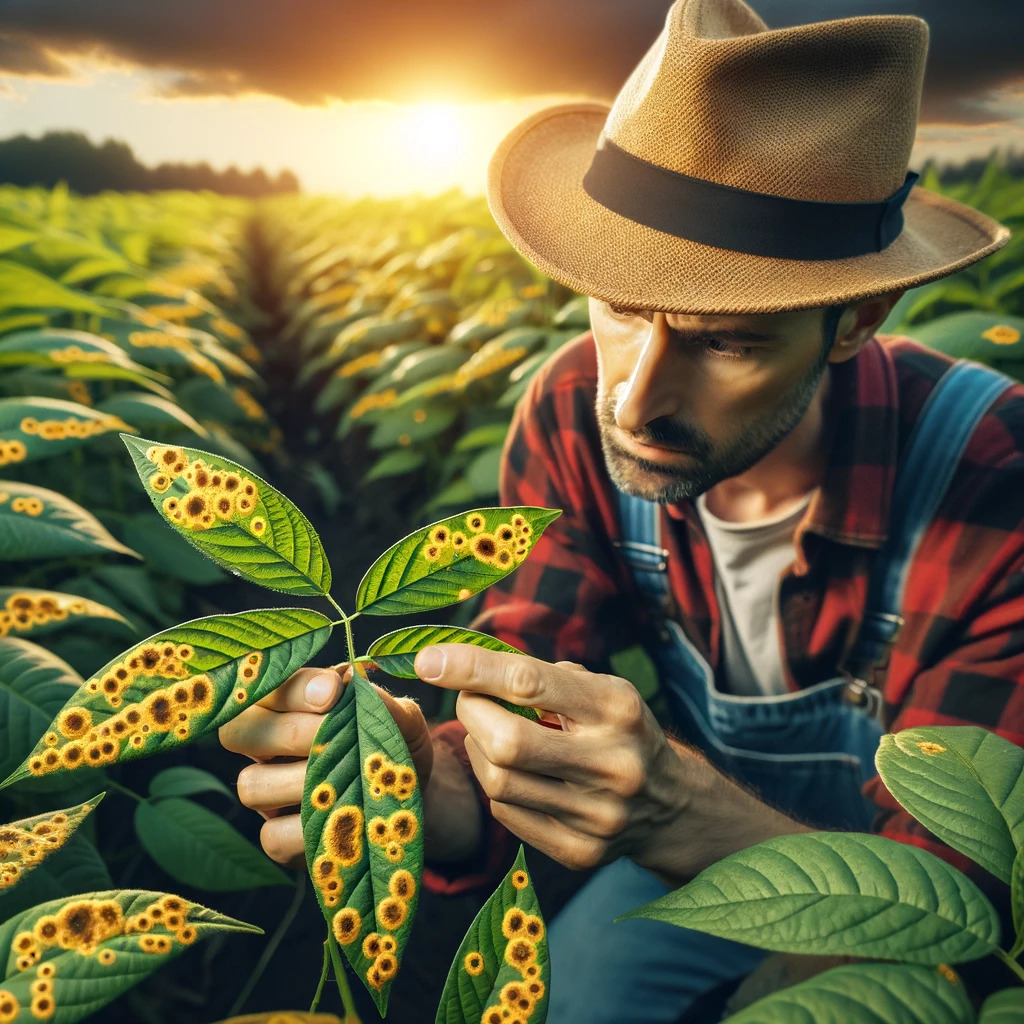

Crops Commonly Affected by Rust
Among the crops most susceptible to rust are:
- Coffee: Coffee rust is one of the most devastating diseases for this crop.
- Wheat and other cereals: Wheat rust can cause significant losses in cereal production.
- Vegetables and fruit trees: Various varieties of rust affect vegetables and fruit trees, limiting their productivity.
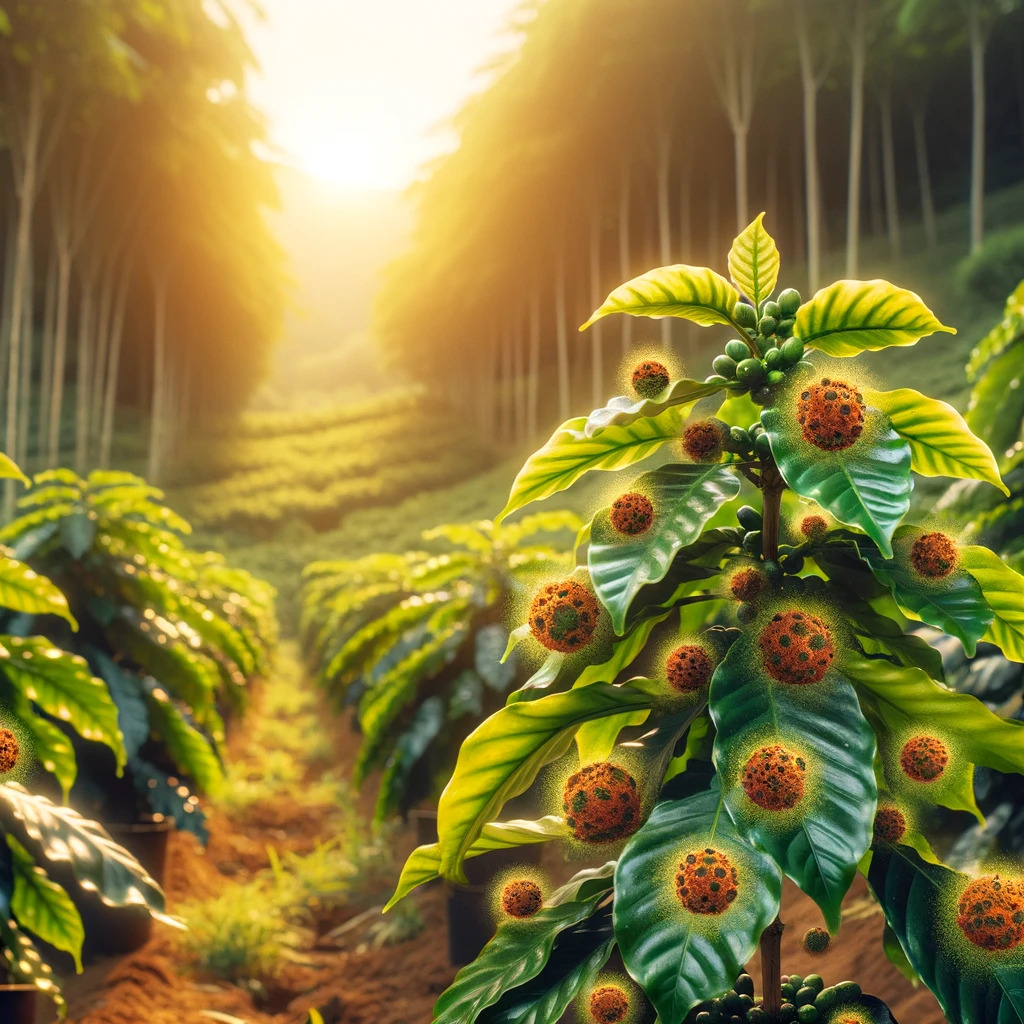

Impact of Rust on Agriculture
Rust not only reduces the photosynthetic capacity of plants but also weakens their growth and development, leading to a noticeable decrease in the quantity and quality of fruits or grains.
Control and Prevention Methods
To manage rust, it is crucial to adopt an integrated approach:
- Selection of resistant varieties: Choose seeds and plants that are resistant to rust.
- Proper cultural practices: Crop rotation, removal of crop residues, and maintaining soil health.
- Chemical and biological control: Use fungicides and biological control agents when necessary.

Success Stories and Field Studies
Around the world, there are examples of how adopting these practices has effectively controlled rust, safeguarding crop yields and quality.
Conclusion: Proactive Strategies for a Sustainable Future in Agriculture
Fighting rust is a key component to ensure sustainability and productivity in agriculture. By adopting integrated management practices and being alert to early signs of the disease, farmers can protect their crops and secure their livelihood.
Advanced Techniques for Rust Control, Impact of Rust on Agricultural Production, Organic Methods Against Rust, Innovations in Rust Treatment, Effective Rust Prevention in Vegetables, Crop Adaptation to Rust Resistance.
 AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog
AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog 