Plant growth-promoting fungi (PGPR) represent a biotechnological solution to maximize crop yields without resorting to harsh chemicals. These fungi interact positively with the roots, stimulating plant growth and protecting against pests. In this article, you will learn what PGPR are, their benefits, main species, and how to use them in modern agriculture.

What are Plant Growth-Promoting Fungi (PGPR)?
PGPR are fungi that improve plant development through various mechanisms, such as the production of phytohormones, nutrient mobilization, and protection against pathogens. They often colonize the rhizosphere and roots, creating a more favorable environment for growth.
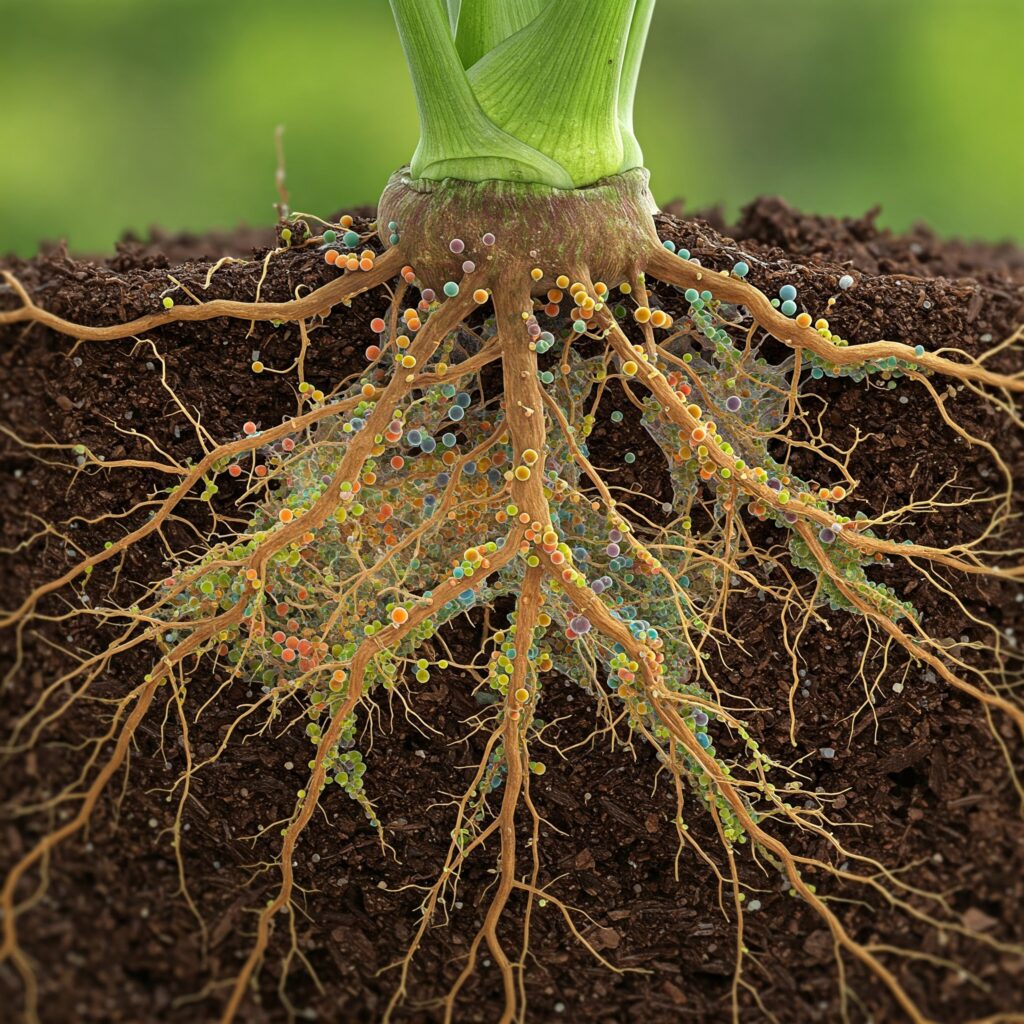

Main species of PGPR and their characteristics
Here are some of the most common plant growth-promoting fungi and their characteristics:
- Beauveria bassiana: In addition to promoting growth, it acts as a biological control of pests, especially soil insects.
- Metarhizium anisopliae: It favors the strengthening of the root system and provides protection against insects such as worms and beetles.
Benefits of PGPR in agriculture
PGPR offer multiple advantages that favor both agricultural production and the sustainable management of natural resources:
- Stimulation of plant growth: They improve the synthesis of hormones such as auxins and gibberellins.
- Biological control of pests: Some PGPR attack insects that damage roots, reducing the use of pesticides.
- Better nutrient uptake: They increase the availability of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other essential elements.
- Strengthening of the root system: More robust roots improve the uptake of water and nutrients.
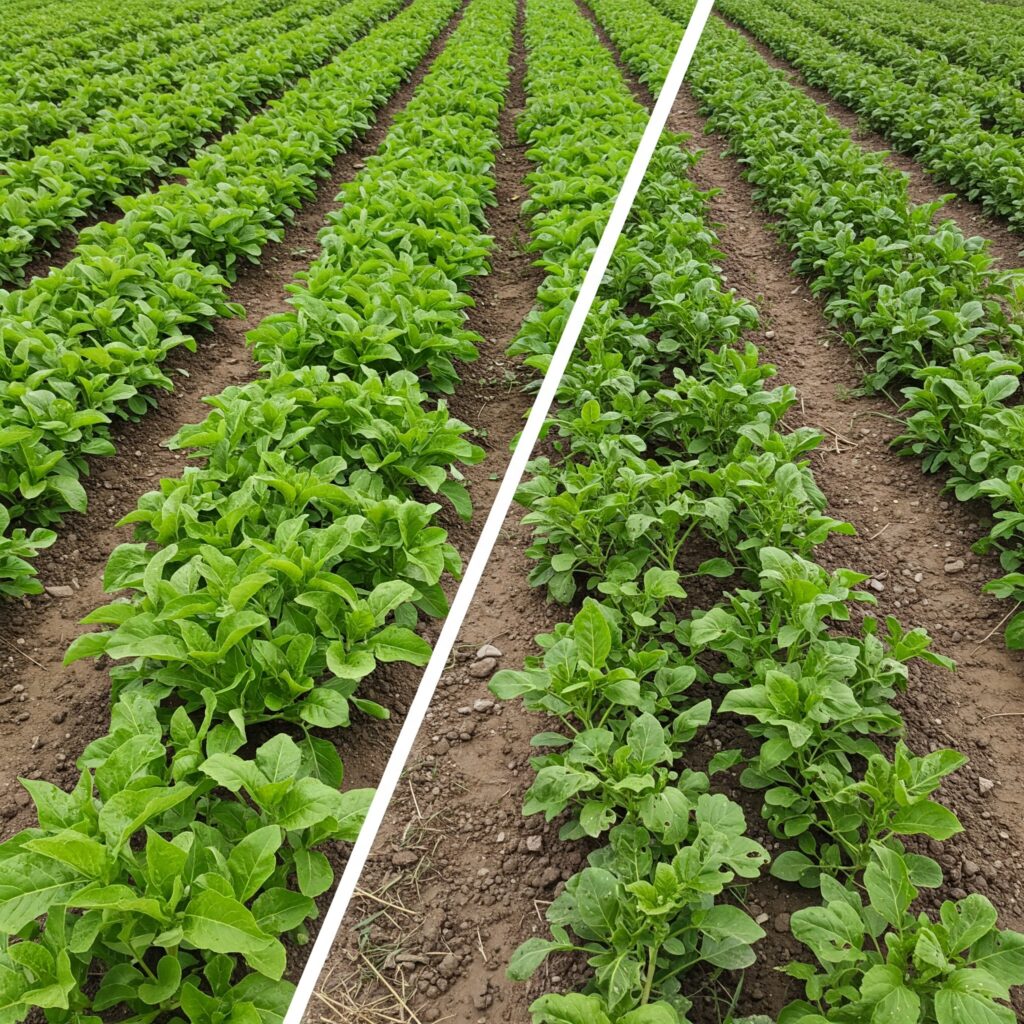

Practical implementation in agricultural crops
To take advantage of the benefits of PGPR, it is advisable to use commercial formulations that contain active spores. Its application can be done by irrigation, seed treatment, or directly into the soil at the time of planting.

Conclusion
Plant growth-promoting fungi represent a key tool to optimize agricultural yield sustainably. Their ability to promote growth and protect crops against pests makes them fundamental allies for modern agricultural production.

References
- Vega, F. E., et al. (2009). Fungal entomopathogens: New insights on their ecological roles. Fungal Ecology, 2(4), 149-159.
- Rangel, D. E. (2011). Stress tolerance in entomopathogenic fungi. Mycological Progress, 10(1), 89-98.
 AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog
AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog 
