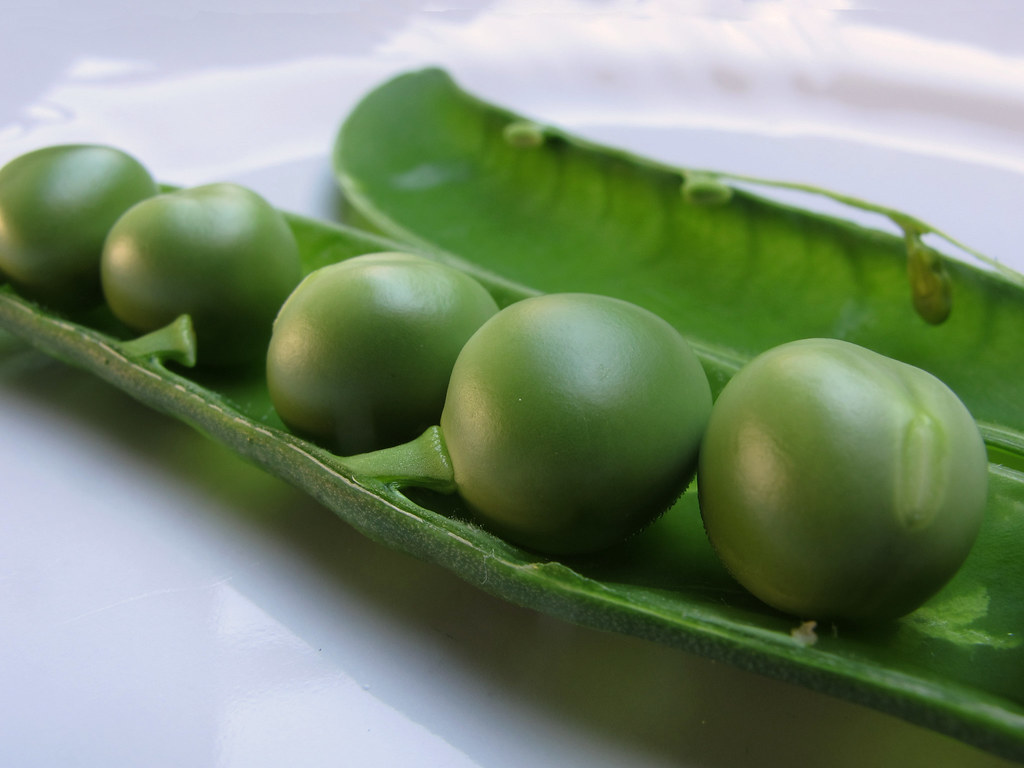
Peas and green beans are crops belonging to the botanical family of legumes. They are products that are consumed fresh, like a vegetable, since when they reach physiological maturity they become seeds and their consumption and uses change with this maturity.
Peas are a legume native to the Middle East, from where it spread to Europe and Asia, becoming popular for its flavor and high nutritional content. Later, its cultivation passed to America, where it became popular in the same way.
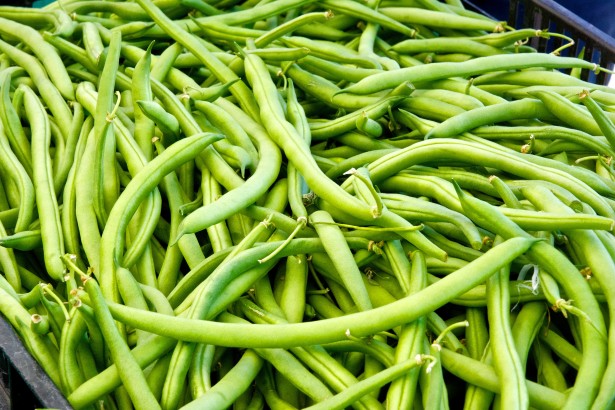

In Mexico, peas are grown in 19 states, the 2017 production reached 63 thousand 934 tons harvested in 11,254.38 hectares, in this area the State of Mexico and Puebla stand out as the leading producers of this legume with 26 thousand 718 tons and 11 thousand 158 tons respectively.
Regarding green beans, in Mexico, the average area planted with this legume between 1993 and 2002 was 8,993 ha, with a variation from 6,368 ha in 1993 to more than 11,000 in 2002; the average yield obtained with green beans during the same period was 7.8 t·ha-1 of young pods. If we consider the production obtained in 2000 and a population of 100 million people, it can be said that in Mexico the annual consumption per person is 1.1 kg of green beans, which is similar to the average observed in other Latin American countries (Silbernagel et al., 1991).
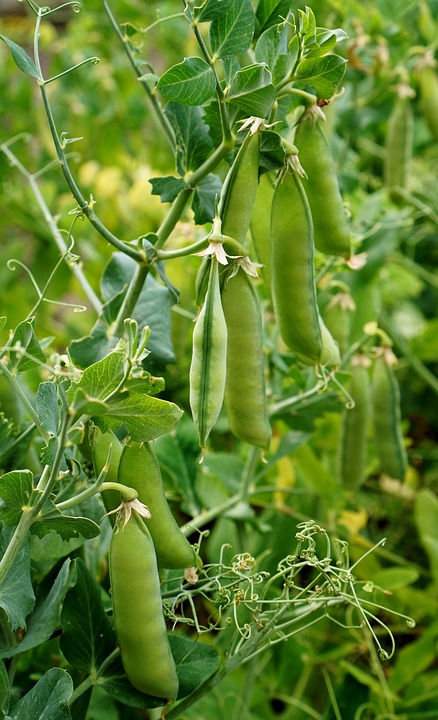

Currently, there is a tendency to increase the consumption of vegetables in the diet, which is why an increase in the demand for green beans is expected nationally and globally. In the US, green bean consumption in 1995 was 3.5 kg per person, between canned, frozen and fresh, and it is estimated that fresh consumption is increasing (Myers, 2000).
 AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog
AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog