Underground crops, including tubers, edible roots, and bulbs, represent a crucial category of food plants that have sustained humanity for millennia. These crops, which grow beneath the soil surface, are essential not only for their nutritional value but also for their adaptability to diverse climatic conditions and their importance in global food security.
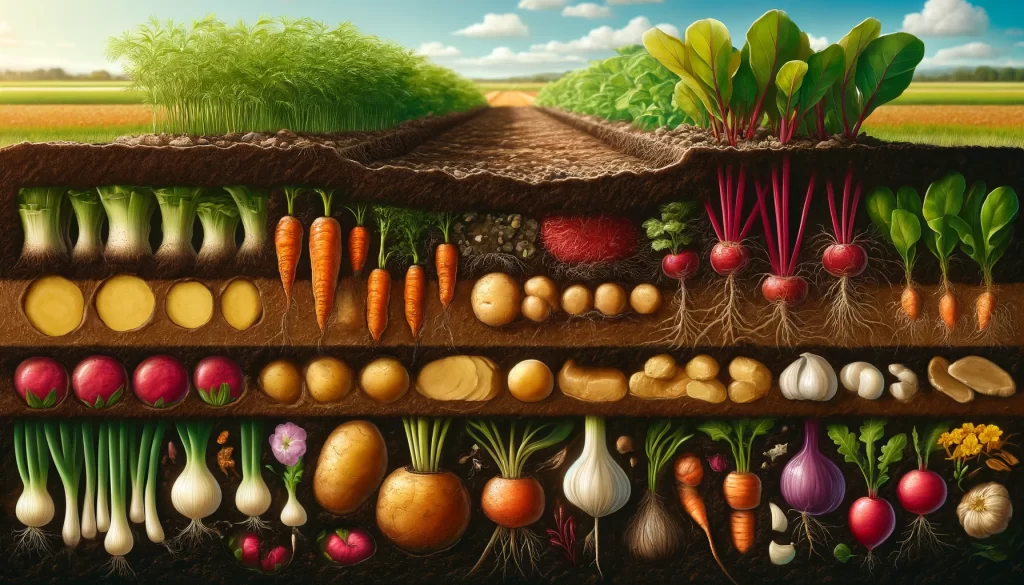

Tubers
Tubers are storage organs that accumulate nutrients in the form of starch. These foods are rich sources of carbohydrates, providing necessary energy for millions of people worldwide.
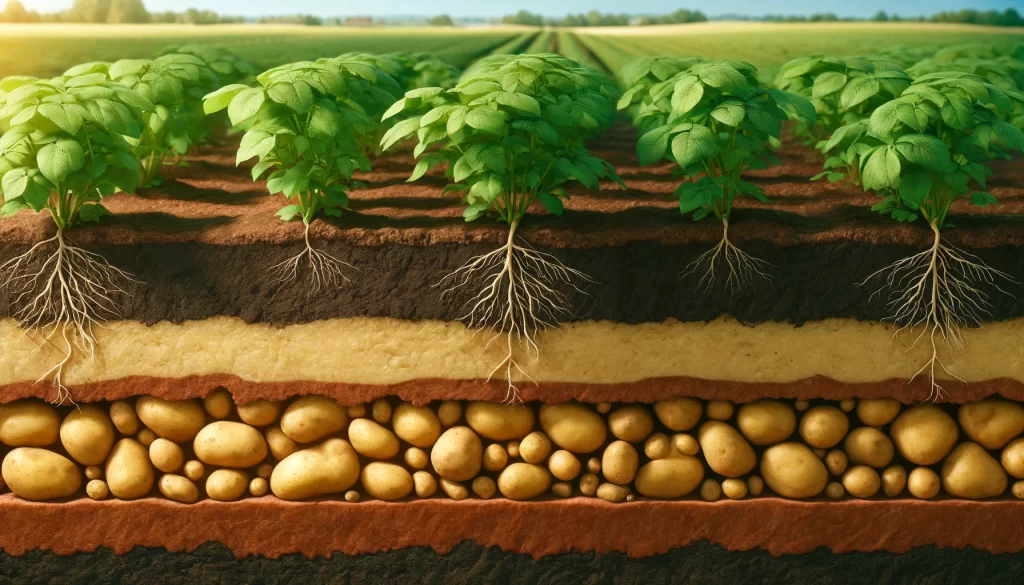

List of Tubers
- Potato (Solanum tuberosum): A widely consumed tuber, with varieties ranging from white to red and purple potatoes. Rich in carbohydrates and vitamin C.
- Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas): A tuber with a sweet taste and flesh that varies in color from orange to purple. High in fiber, vitamins A and C, and antioxidants.
- Yuca or Cassava (Manihot esculenta): A long brown tuber with white flesh. An important carbohydrate source in tropical regions, it must be properly cooked to eliminate toxic compounds.
- Yam (Dioscorea spp.): An elongated tuber with rough skin and white, yellow, or purple flesh. Consumed boiled, roasted, or in soups and stews.
- Oca (Oxalis tuberosa): A small tuber with smooth skin and bright colors, native to the Andes. Sweet and tangy flavor.
- Mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum): An Andean tuber similar to oca, but with a stronger and spicier flavor.
- Arracacha (Arracacia xanthorrhiza): A tuber similar to a carrot with a sweet and starchy flavor.
- Jicama (Pachyrhizus erosus): A crunchy and sweet tuber with brown skin and white flesh.
- Jerusalem Artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus): A knobby tuber with a flavor similar to artichoke.
- Taro (Colocasia esculenta): A brown tuber with white or purple flesh, a staple food in many tropical cultures.
- Malanga (Xanthosoma spp.): Similar to taro, with a firmer texture and slightly nutty flavor.
- Ulluco (Ullucus tuberosus): A small Andean tuber with bright colors and a waxy texture.
- Tiger Nut (Cyperus esculentus): A small, sweet tuber also known as “chufa.”
- Belembe (Xanthosoma sagittifolium): A tropical tuber with a texture similar to taro.
Edible Roots
Edible roots are known for their nutritional density, providing vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. These vegetables not only improve digestive health but also offer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. Their colorful and varied flavors make them indispensable in salads, soups, and stews.
List of Edible Roots
- Carrot (Daucus carota): An orange root, though there are purple, yellow, and white varieties. Rich in beta-carotene (vitamin A).
- Beetroot (Beta vulgaris): A deep red root, rich in antioxidants and nutrients such as folic acid.
- Radish (Raphanus sativus): A small, round root with a spicy flavor, available in red, white, and black varieties.
- Turnip (Brassica rapa): A round, white root with purple accents, with a mild, slightly sweet flavor.
- Parsnip (Pastinaca sativa): A long, white root, similar to a carrot but with a sweeter, earthier flavor.
- Yautia or Malanga (Xanthosoma spp.): A brown root with white or purple flesh, used in many tropical cuisines.
- Jicama (Pachyrhizus erosus): A crunchy, sweet root with brown skin and white flesh.
- Celery Root (Apium graveolens var. rapaceum): A round, knobby root with a celery flavor.
- Parsley Root (Petroselinum crispum var. tuberosum): Similar to parsnip, with a milder, more delicate flavor.
- Burdock Root (Arctium lappa): A long, thin root with a sweet, earthy flavor.
- Yuca or Cassava (Manihot esculenta): A long root with brown skin and white flesh.
- Lotus Root (Nelumbo nucifera): A segmented, edible root with a mild flavor.
- Turmeric Root (Curcuma longa): A small, orange root with an earthy, spicy flavor.
- Ginger Root (Zingiber officinale): A knobby root with a strong, spicy flavor.
- Fennel Root (Foeniculum vulgare): A bulbous root with a licorice-like flavor.
- Celeriac (Apium graveolens var. rapaceum): A round root with a rough skin and creamy flesh.
- Dandelion Root (Taraxacum officinale): A long, thin root with medicinal properties.
- Maca Root (Lepidium meyenii): An Andean root with energetic and nutritional properties.
Bulbs
Bulbs are essential in cooking for their ability to enhance flavors and provide health benefits. With antibacterial properties and sulfur compounds, these vegetables not only improve the taste of dishes but also contribute to cardiovascular health and strengthen the immune system.
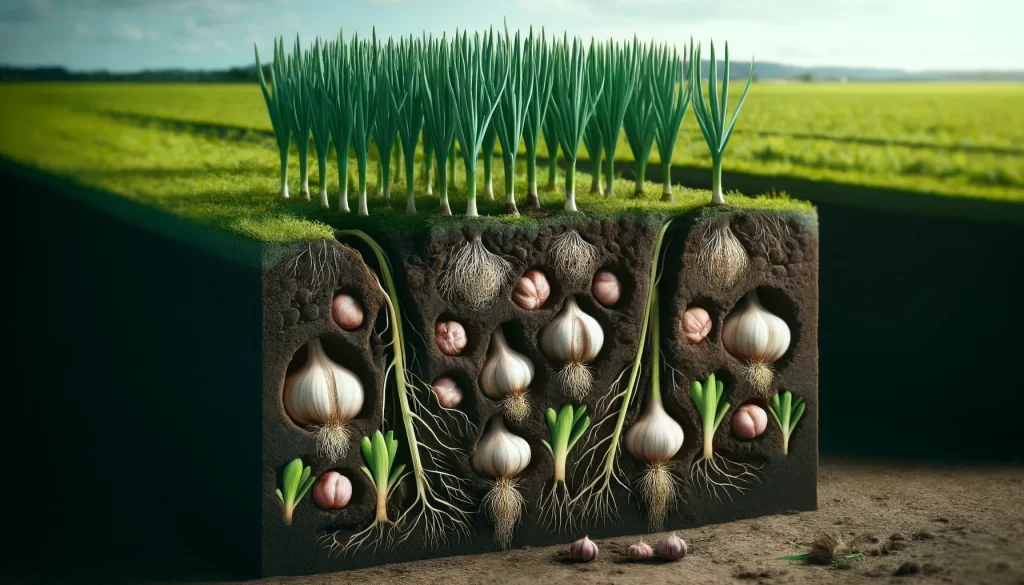

List of Edible Bulbs
- Onion (Allium cepa): A bulb with concentric layers and a flavor ranging from sweet to spicy. One of the most used ingredients in global cuisine.
- Garlic (Allium sativum): A bulb composed of multiple cloves, with a strong, distinctive flavor. Used both as a condiment and for its medicinal properties.
- Leek (Allium ampeloprasum): A long, cylindrical bulb with a mild, onion-like flavor but more delicate.
- Shallot (Allium ascalonicum): A small, elongated bulb with a sweeter, milder flavor than onion.
- Spring Onion (Allium fistulosum): A small, elongated bulb, mainly used for its green stalks and mild flavor.
- Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare): A white, crunchy bulb with a licorice-like flavor. Used both raw in salads and cooked in various preparations.
- Saffron (Crocus sativus): A bulb from which the red stigmas are used as a spice, known for its distinctive flavor and use in gourmet cooking.
- Daylily (Hemerocallis spp.): A bulb whose flower buds are consumed, especially in Asian cuisine.
- Pearl Onion (Allium ampeloprasum var. sectivum): A small, round bulb, ideal for pickling and garnishes due to its mild, sweet flavor.
- Black Salsify (Scorzonera hispanica): A long, black-skinned bulb with white flesh, known for its slightly sweet flavor and tender texture.
 AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog
AgronoBlog – Agriculture Blog 


